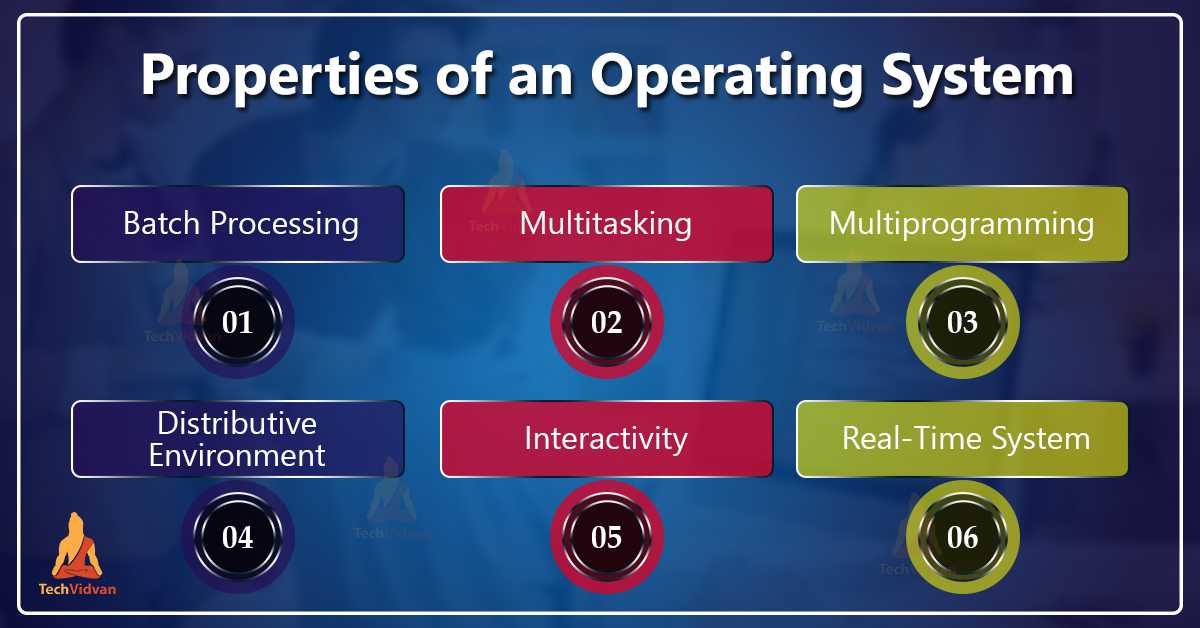
Batch Processing: Batch processing is a technique in which an Operating System collects the programs and data together in a batch before processing starts.
Multitasking: Multitasking is when multiple jobs are executed by the CPU simultaneously by switching between them.
Multiprogramming: Sharing the processor, when two or more programs reside in memory at the same time, is referred to as multiprogramming.
Interactivity: Interactivity refers to the ability of users to interact with a computer system.
Real-Time System: Real-time systems are usually dedicated, embedded systems. The Operating system must guarantee a response to events within fixed periods of time to ensure correct performance.
Distributed Environment: A distributed environment refers to multiple independent CPUs or processors in a computer system. The OS distributes computation logic among several physical processors. The processors do not share a memory or a clock. Instead, each processor has its own local memory. The OS manages the communications between the processors.
Spooling: Spooling is an acronym for simultaneous peripheral operations on-line. Spooling refers to putting data of various I/O jobs in a buffer. This buffer is a special area in memory or hard disk which is accessible to I/O devices.
Comments
Post a Comment